Add /Bin To Your $Path Variable UPDATED
Add /Bin To Your $Path Variable

past Navindu Jayatilake
How to become started with MongoDB in 10 minutes

MongoDB is a rich document-oriented NoSQL database.
If you lot are a complete beginner to NoSQL, I recommend you to accept a quick await at my NoSQL article published previously.
Today, I wanted to share some of the basic stuff about MongoDB commands such equally querying, filtering data, deleting, updating and and then on.
Okay, enough of the talk, permit's go to work!
Configuration ?
In order to work with MongoDB, commencement you demand to install MongoDB on your computer. To do this, visit the official download center and download the version for your specific OS. Here, I've used Windows.
After downloading MongoDB customs server setup, yous'll get through a 'next later next' installation procedure. In one case done, head over to the C drive in which yous take installed MongoDB. Get to program files and select the MongoDB directory.
C: -> Program Files -> MongoDB -> Server -> 4.0(version) -> bin In the bin directory, you'll observe an interesting couple of executable files.
- mongod
- mongo
Allow'south talk about these two files.
mongod stands for "Mongo Daemon". mongod is a background process used by MongoDB. The chief purpose of mongod is to manage all the MongoDB server tasks. For example, accepting requests, responding to client, and retentivity management.
mongo is a command line shell that can interact with the client (for example, arrangement administrators and developers).
Now let's run into how we can get this server upwards and running. To do that on Windows, showtime y'all demand to create a couple of directories in your C drive. Open up up your command prompt within your C drive and do the post-obit:
C:\> mkdir data/dbC:\> cd dataC:\> mkdir db The purpose of these directories is MongoDB requires a folder to store all data. MongoDB'due south default information directory path is /data/db on the drive. Therefore, it is necessary that we provide those directories like and so.
If you lot start the MongoDB server without those directories, you'll probably see this following error:
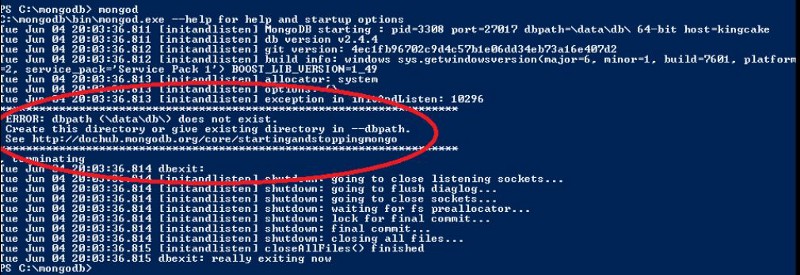
After creating those 2 files, head over over again to the bin folder y'all have in your mongodb directory and open up upwardly your shell inside information technology. Run the following command:
mongod Voilà! Now our MongoDB server is upwardly and running! ?
In order to piece of work with this server, we need a mediator. So open another command window inside the bind binder and run the following command:
mongo Subsequently running this command, navigate to the vanquish which we ran mongod command (which is our server). Yous'll meet a 'connection accepted' message at the terminate. That means our installation and configuration is successful!
Just simply run in the mongo shell:
db 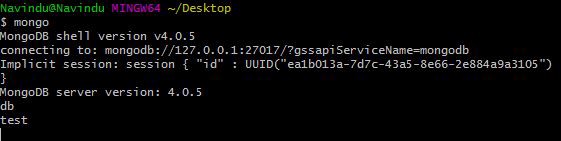
Setting up Environment Variables
To save time, you tin set up your environs variables. In Windows, this is washed by following the menus below:
Advanced System Settings -> Environs Variables -> Path(Under System Variables) -> Edit But copy the path of our bin folder and hit OK! In my case it's C:\Plan Files\MongoDB\Server\4.0\bin
At present you're all set!
Working with MongoDB
There'southward a agglomeration of GUIs (Graphical User Interface) to work with MongoDB server such as MongoDB Compass, Studio 3T then on.
They provide a graphical interface and so you can easily work with your database and perform queries instead of using a trounce and typing queries manually.
But in this article we'll be using command prompt to do our work.
Now it'due south fourth dimension for us to dive into MongoDB commands that'll help you to use with your future projects.
- Open upwards your command prompt and type
mongodto start the MongoDB server.
2. Open upwardly another vanquish and type mongo to connect to MongoDB database server.
1. Finding the electric current database you're in
db 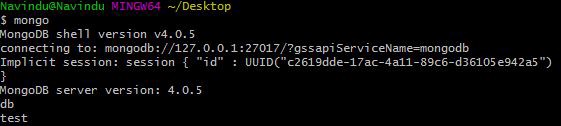
This command will show the current database you lot are in. test is the initial database that comes by default.
two. Listing databases
show databases 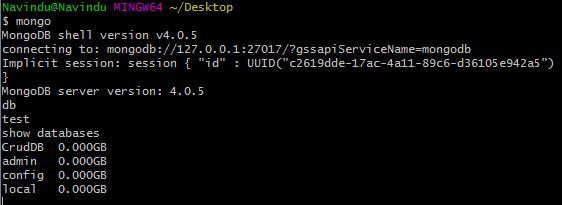
I currently have four databases. They are: CrudDB, admin, config and local.
iii. Go to a particular database
utilize <your_db_name> 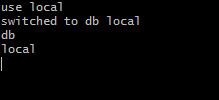
Here I've moved to the local database. You can check this if you attempt the command db to impress out the electric current database name.
four. Creating a Database
With RDBMS (Relational Database Management Systems) we have Databases, Tables, Rows and Columns.
Simply in NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB, data is stored in BSON format (a binary version of JSON). They are stored in structures chosen "collections".
In SQL databases, these are like to Tables.
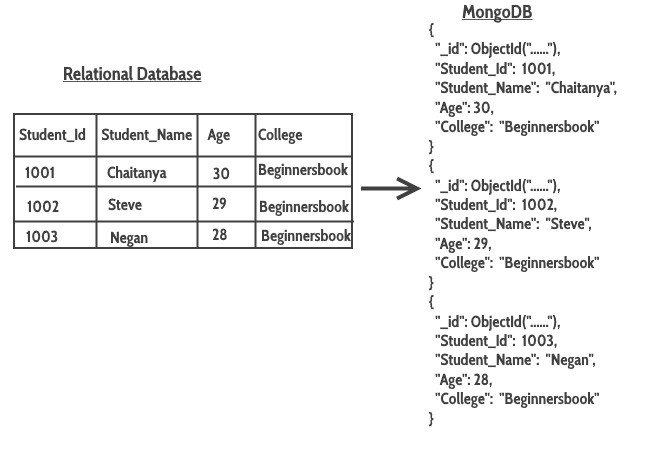
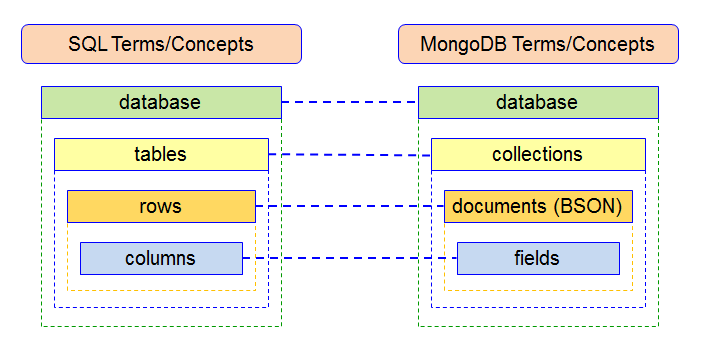
Alright, let's talk almost how nosotros create a database in the mongo beat.
use <your_db_name> Look, nosotros had this command before! Why am I using information technology once more?!
In MongoDB server, if your database is present already, using that command volition navigate into your database.
But if the database is not present already, then MongoDB server is going to create the database for you. And then, it volition navigate into information technology.
Afterward creating a new database, running the testify database command volition not show your newly created database. This is because, until it has any data (documents) in it, it is non going to bear witness in your db list.
5. Creating a Collection
Navigate into your newly created database with the use command.
Really, there are ii ways to create a collection. Let's run into both.
One mode is to insert information into the collection:
db.myCollection.insert({"proper noun": "john", "age" : 22, "location": "colombo"}) This is going to create your collection myCollection even if the drove does not exist. Then it will insert a document with name and age. These are not-capped collections.
The 2d way is shown below:
2.1 Creating a Non-Capped Collection
db.createCollection("myCollection") 2.2 Creating a Capped Collection
db.createCollection("mySecondCollection", {capped : true, size : 2, max : 2}) In this manner, you lot're going to create a collection without inserting data.
A "capped collection" has a maximum document count that prevents overflowing documents.
In this case, I take enabled capping, by setting its value to true.
The size : 2 ways a limit of two megabytes, and max: 2 sets the maximum number of documents to two.
At present if you try to insert more than two documents to mySecondCollection and employ the discover command (which nosotros will talk near shortly), you'll only run across the most recently inserted documents. Keep in mind this doesn't mean that the very start document has been deleted — it is but not showing.
six. Inserting Data
We tin insert information to a new collection, or to a collection that has been created before.
There are three methods of inserting data.
-
insertOne()is used to insert a single certificate only. -
insertMany()is used to insert more than 1 document. -
insert()is used to insert documents as many as you want.
Below are some examples:
- insertOne()
db.myCollection.insertOne( { "name": "navindu", "historic period": 22 } ) - insertMany()
db.myCollection.insertMany([ { "name": "navindu", "age": 22 }, { "proper noun": "kavindu", "historic period": 20 }, { "name": "john doe", "age": 25, "location": "colombo" } ]) The insert() method is similar to the insertMany() method.
Besides, notice nosotros have inserted a new property called location on the certificate for John Doe . So if you employ observe , then you'll see just for john doe the location property is attached.
This can exist an advantage when it comes to NoSQL databases such as MongoDB. Information technology allows for scalability.

seven. Querying Data
Here'due south how yous can query all data from a drove:
db.myCollection.detect() 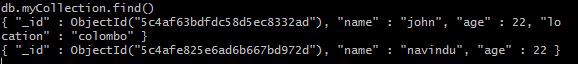
If you want to see this information in a cleaner, mode just add together .pretty() to the end of it. This volition brandish document in pretty-printed JSON format.
db.myCollection.find().pretty() 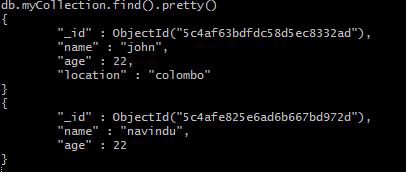
Expect...In these examples did you just notice something like _id? How did that get there?
Well, whenever you insert a certificate, MongoDB automatically adds an _id field which uniquely identifies each document. If you do not desire it to display, just only run the following command
db.myCollection.discover({}, _id: 0).pretty() Side by side, we'll look at filtering data.
If you want to display some specific document, yous could specify a unmarried detail of the document which you want to exist displayed.
db.myCollection.detect( { name: "john" } ) 
Let's say yous want but to display people whose age is less than 25. Y'all can employ $lt to filter for this.
db.myCollection.notice( { historic period : {$lt : 25} } ) Similarly, $gt stands for greater than, $lte is "less than or equal to", $gte is "greater than or equal to" and $ne is "non equal".
8. Updating documents
Let'due south say y'all want to update someone'due south accost or age, how yous could do it? Well, come across the adjacent example:
db.myCollection.update({age : twenty}, {$gear up: {age: 23}}) The first argument is the field of which certificate you want to update. Here, I specify age for the simplicity. In product environment, you could utilize something like the _id field.
It is always better to use something similar _id to update a unique row. This is considering multiple fields can have same historic period and name. Therefore, if you update a single row, information technology will affect all rows which have aforementioned name and age.
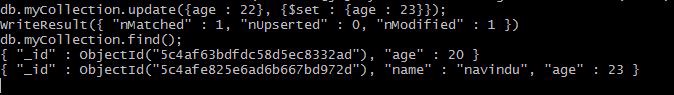
If you update a certificate this way with a new belongings, let'south say location for example, the document will be updated with the new attribute. And if yous do a detect, then the consequence will be:
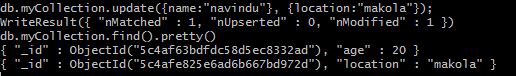
If you need to remove a belongings from a single document, you could do something like this (let's say you want age to be gone):
db.myCollection.update({name: "navindu"}, {$unset: age}); nine. Removing a document
As I have mentioned earlier, when you update or delete a document, you just demand specify the _id not just name, age, location.
db.myCollection.remove({proper noun: "navindu"}); 10. Removing a collection
db.myCollection.remove({}); Note, this is not equal to the drop() method. The difference is drop() is used to remove all the documents inside a collection, simply the remove() method is used to delete all the documents along with the collection itself.
Logical Operators
MongoDB provides logical operators. The picture beneath summarizes the different types of logical operators.
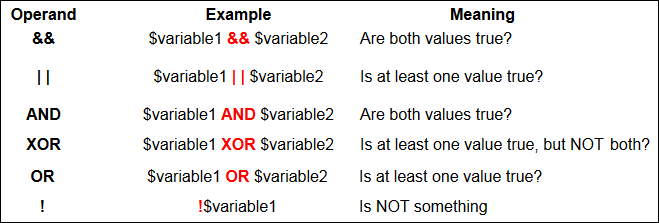
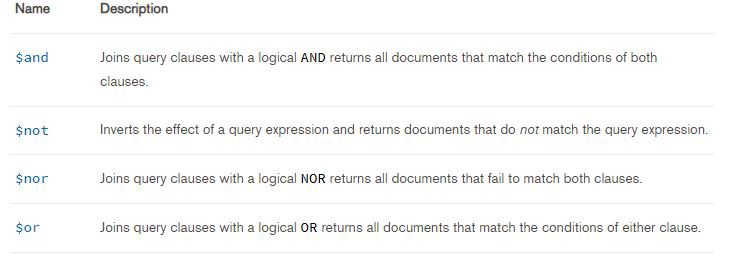
Let'south say y'all want to display people whose age is less than 25, and likewise whose location is Colombo. What we could do?
We can use the $and operator!
db.myCollection.find({$and:[{age : {$lt : 25}}, {location: "colombo"}]}); Last only non to the lowest degree, permit's talk about aggregation.
Aggregation
A quick reminder on what we learned nigh aggregation functions in SQL databases:
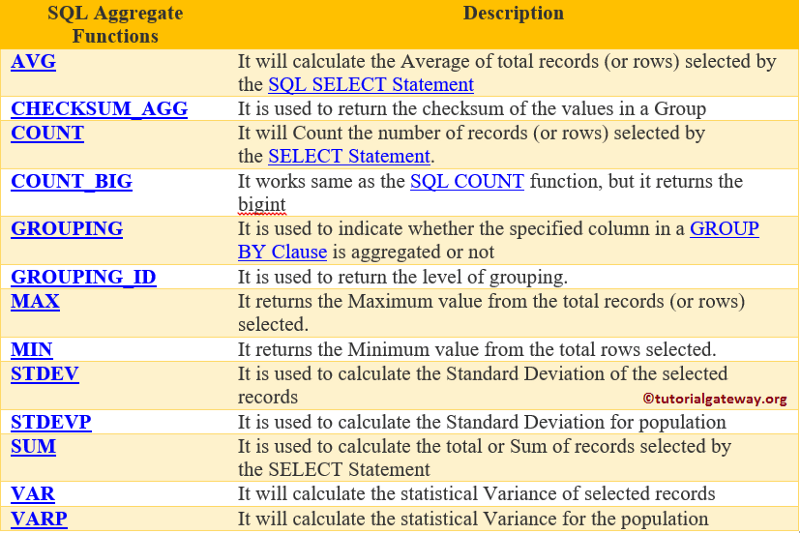
Simply put, aggregation groups values from multiple documents and summarizes them in some way.
Imagine if we had male and female students in a recordBook collection and we want a total count on each of them. In order to go the sum of males and females, we could use the $group aggregate office.
db.recordBook.aggregate([ { $group : {_id : "$gender", outcome: {$sum: ane}} } ]); 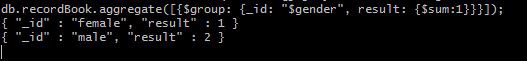
Wrapping upwards
So, we have discussed the basics of MongoDB that you might need in the hereafter to build an awarding. I hope you enjoyed this article – thank you for reading!
If you have any queries regarding this tutorial, feel gratis to comment out in the comment section below or contact me on Facebook or Twitter or Instagram.
See you lot guys in the next article! ❤️ ✌?
Link to my previous article: NoSQL
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp'south open source curriculum has helped more than xl,000 people get jobs every bit developers. Get started
DOWNLOAD HERE
Posted by: jacksonstento.blogspot.com
